This beautiful video of fluorescence microscopy was captured using the HDCAM5 microscope camera.
Contact Microscope World with questions regarding fluorescence microscopy or capturing images and video of fluorescence microscopy.
Microscope information, images from beneath the microscope and educational science projects.
Tuesday, October 16, 2018
Wednesday, October 10, 2018
Protozoan Parasite under the Microscope
OE (Ophryocystis Elektroscirrha) is a protozoan parasite that infects butterflies in the Danaus species group, those that host on milkweed. This photo of some Monarch butterfly abdominal scales was taken by Rob Wood with a Canon 80D DSLR through a Richter Optica HS-3 Biological microscope, at 400X. The large objects are scales, while the football-shaped objects are OE spores. Each spore contains 8 protozoa.
 |
| Ophryocystis Elektroscirrha under the HS-3 microscope. |
Thank you Rob for sharing this photo with Microscope World!
Monday, September 17, 2018
Woody Stem Under the Microscope
Below is a woody stem cross section captured under the Richter Optica UX1 cordless student microscope captured at 400x magnification. This image was captured using the DCM5 microscope camera (5.2 megapixels).
The woody stem produces wood as its structural tissue - typically either a tree, shrub or liana.
The woody stem produces wood as its structural tissue - typically either a tree, shrub or liana.
 |
| Woody stem c.s. under the UX1 cordless microscope with DCM5 camera. |
Tuesday, May 22, 2018
pco Cameras
Microscope World is proud to offer pco scientific cameras. The pco cameras are known for their low readout noise, high frame rates and exposure times that range from nanoseconds to hours. UV and NIR detection and high dynamic range are just some of the pco cameras' unique core competences.
The pco.panda 4.2 camera combines revolutionary sCMOS technology in a compact design. High quantum efficiency (up to 80%) and low readout noise make this camera suitable for countless applications. The USB 3.1 interface enables ultra-speed data transfer and direct power via the USB cable, making external power supplies redundant. Frame rate = 40 fps @ full resolution 2048 x 2048, 80 fps @ 2048 x1024.
 |
| pco.panda 4.2 Camera |
The pco.panda 4.2 camera combines revolutionary sCMOS technology in a compact design. High quantum efficiency (up to 80%) and low readout noise make this camera suitable for countless applications. The USB 3.1 interface enables ultra-speed data transfer and direct power via the USB cable, making external power supplies redundant. Frame rate = 40 fps @ full resolution 2048 x 2048, 80 fps @ 2048 x1024.
The pco.edge 3.1 camera has a sCMOS sensor and is designed for users who require high resolution and high frame rates. This USB3 camera is available in color or monochrome. 50 fps @ full resolution 2048 x 1536, 75 fps @ 1280 x 1024, 160 fps @ 640 x 480.
The pco.edge 4.2 camera has sCMOS technology and can be optionally upgraded with a water cooling system. This camera has high quantum efficiency at up to 82% at peak. 100 fps @ RS fast scan 2048 x 2048, 189 fps @ fast scan 1920 x 1080, 420 fps @ fast scan 640 x 480 when using camera link.
The pco.edge 4.2 LT camera has sCMOS technology and USB3 output. High quantum efficiency of up to 82% at peak. 40 fps @ full resolution 2048 x 2048, 80 fps @ 1280 x 1024, and 170 fps @ 640 x 480.
The pco.edge 5.5 camera has sCMOS technology and can be optionally upgraded with a water cooling system. Quantum efficiency of > 60% @ peak. With camera link, the frame rates are high: 100 fps @ RS/GR fast scan 2560 x 2160, 201 fps @ fast scan 1920 x 1080, 450 fps @ fast scan 640 x 480.
Wednesday, May 16, 2018
Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy is a tool used in biology, material science, and biomedical sciences. The fluorescence microscope can reveal the presence of a single molecule. The basic function of a fluorescence microscope is to irradiate the specimen with a desired and specific band of wavelengths, and then to separate the much weaker emitted fluorescence from the excitation light.
The fluorescence microscopy images shown below were captured using the Fein Optic RB30-GFP fluorescence microscope and the Lumenera Infinity 3S-1UR microscope camera.
The fluorescence microscopy images shown below were captured using the Fein Optic RB30-GFP fluorescence microscope and the Lumenera Infinity 3S-1UR microscope camera.
 |
| Fluorescence microscopy image captured using a 60x objective lens. |
 |
| Fluorescence microscope image, 600x. |
Contact Microscope World with questions regarding fluorescence microscopy.
Thursday, April 19, 2018
Spring Flowers under the Microscope
In the spirit of welcoming spring, below are some photos of flowers captured under the biological microscope and stereo microscope.
 |
| Convallaria (Lily of the Valley) captured with Zeiss Primostar HD microscope, 400x. |
 |
| Monocot under a student microscope, 100x. |
 |
| Flower captured with a stereo microscope. |
Wishing you a beautiful spring!
Thursday, February 15, 2018
How to Set Up Koehler Microscope Illumination Properly
There are two key areas on a compound biological microscope with Koehler illumination that need to be adjusted in order to set up the Koehler illumination properly: field diaphragm and aperture diaphragm.
The microscope's aperture diaphragm can be found on the condenser of the microscope and it is typically a lever that is adjusted, or a built-in slider on the condenser.
You can learn more about Koehler illumination and setup here.
The microscope's aperture diaphragm can be found on the condenser of the microscope and it is typically a lever that is adjusted, or a built-in slider on the condenser.
 |
| This is the RB40 microscope, the arrow points to the aperture diaphragm. |
The aperture diaphragm on the microscope will usually have numbers on it that correlate to the numerical aperture (N.A.) on your objective lenses.
 |
| Aperture diaphragm on the microscope condenser. |
Setting up Koehler Illumination
- Start by adjusting the field diaphragm (on the bottom of the microscope where the light is). Focus on your image and open the field diaphragm all the way up so lots of light shines through.
- Close the aperture diaphragm (on the condenser) down so you can see the edges of it. Is this dark circle centered in your field of view? If not, use the small centering screws on either side of the condenser to move the circle into the center.
- Open the aperture diaphragm back up until the image contrast is sharp and the edges of the aperture diaphragm are crisp and clear.
You can learn more about Koehler illumination and setup here.
Wednesday, January 31, 2018
High School Microscope HS-3
Richter Optica recently introduced the new HS-3 high school microscope. This student microscope has several features that make it appealing to both teachers and students.
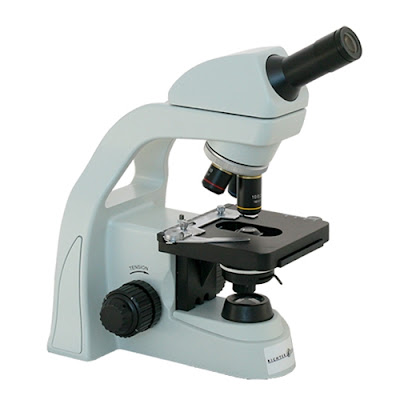 |
| HS-3 High School Microscope |
This high school microscope has a head that rotates 360°, making it easy for students to share the microscope. Teachers like the wider base to help avoid tip-over risk and the locked-on eyepiece. Key microscope features include:
- Built-in mechanical stage
- Cool LED illumination, that is rechargeable and can run corded or cordless.
- Cord holder
- Coarse & Fine focusing for crisp images
- 40x, 100x, 400x, and 1000x magnification
- Operate corded or cordless
Thursday, January 11, 2018
Protists under the Microscope
Protists are any member of a group of diverse eukaryotic unicellular microscopic organisms. Protist typically refers to a eukaryote that is not a true animal, plant or fungus because it lacks a multicellular stage.
In order to view protists, a biological microscope is required with 400x magnification.
The image below of a protist was captured using a sample of pond water under the Zeiss Primostar HD digital microscope.
In order to view protists, a biological microscope is required with 400x magnification.
The image below of a protist was captured using a sample of pond water under the Zeiss Primostar HD digital microscope.
 |
| Protist captured under a digital biological microscope. |
For more information on protists visit Rutgers University page.
Contact Microscope World with microscopy questions.
